Introduction

As IoT devices multiply around us—from simple sensors to complex industrial equipment—security has become a major problem. These connected devices are increasingly targeted by attackers, and the traditional approach of relying on centralized servers run by big companies creates single points of failure and privacy concerns. We needed something better.
With years of practical experience in creating IoT systems and working with microcontrollers such as ESP32 and RISC-V, we thought there had to be a simple and secure method to address this growing problem. We understood that blockchain could provide the decentralized security layer that these devices need, ensuring data integrity and communication security without relying on centralized authorities.
After looking at different blockchain options, we chose to build on Ravencoin's codebase. Here's why:
- With our changes: Modifying the code to optimize it to our needs is one of the many reasons why we have created a blockchain from scratch.
- Built for Assets: The Ravencoin code has a native system for creating and managing tokens and NFTs efficiently, without the complexity and security risks of smart contracts.
- Bitcoin's DNA: We inherit Bitcoin's proven, battle-tested security foundation—code that's been protecting billions of dollars for over a decade.
- Fair Mining: GPU-friendly mining keeps the network decentralized. No ASICs means no mining monopolies, creating a more democratic ecosystem.
To better understand the purpose of Neurai, it is necessary to understand each of the important points that comprise it and that together create the Neurai ecosystem. Here is a list and explanation of these points:
Blockchain
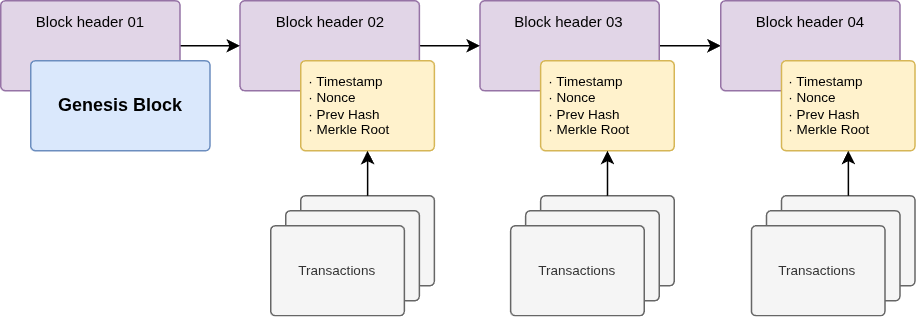
Blockchain is a digital ledger that's distributed across many computers in a peer-to-peer network. Think of it as a shared database that no single person or company controls. The name comes from its structure: blocks of data linked together in a chain.
Each block records transactions—who sent what to whom, when, and other details. What makes blockchain revolutionary is its permanence: once a block is added, it's practically impossible to change, hack, or cheat. The data stays there forever.
As this information is distributed and highly difficult to modify over time, it allows for the guarantee of information over time, such as assets with functions for DePIN, unique identification, IoT devices, transactions, and other needs that can be covered by these features.
IoT
IoT (Internet of Things) is all the physical devices around the world that connect to the internet to collect and share data. It's about making everyday objects smarter—from your thermostat to industrial sensors—blending the physical and digital worlds. You can buy ready-made IoT devices, or build your own using affordable microcontrollers like ESP32 or RISC-V boards.
As we mentioned at the beginning, these IoT devices can be connected directly to the Internet or indirectly through hubs. In either case, they can be easily attacked because they are not updated, the equipment is outdated, companies disappear without leaving support, and proprietary systems always depend on a third party.
Our goal is to provide a secure and private encryption system that will stand the test of time, currently adjusted with AES-256, but easily adaptable to a post-quantum algorithm.
The DePIN messaging system guarantees this transfer of information, either directly between IoT devices using the Neurai blockchain or using a link hub and enabling post-quantum encryption.
DePIN
DePIN stands for Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks. In the blockchain world, DePIN represents a shift from traditional centralized infrastructure—owned and controlled by large corporations—to a distributed model where physical infrastructure is built, operated, and maintained by networks of independent participants. Think of it as Uber for infrastructure: instead of one company owning all the hardware, many people contribute resources and get rewarded for their participation.
In Neurai's context, DePIN enables IoT devices to form decentralized networks that can communicate, verify identity, and transact without relying on centralized servers or cloud providers. This means your smart sensors, industrial equipment, or home automation devices can operate securely and privately, coordinating directly with each other through the blockchain—no middleman required. The DePIN messaging protocol in Neurai uses military-grade encryption (AES-256) to ensure that device communications remain private and secure, even as they participate in a fully decentralized network.
Since the system does not depend on anyone, you can manage the node that serves to manage messages yourself. These messages are ephemeral and are not stored on the blockchain, but the authenticity of the participants is verified thanks to their public keys. MCP servers can be integrated into this system to use AI and control remote equipment in various ways without the need for complex VPN or proxy protocols.
AI
In recent years, AI models have exploded significantly, with powerful proprietary models such as Gemmini, ChatGPT, Claude, and Grok, but also free models that are very similar to the latter, such as Deepseek, Qwen, Mistral, and Olmo.
OpenSource models require large machines to run, but offer the benefit of privacy and information security. Small 4B models can be easily configured with small computers with 32GB of RAM and a recent CPU, which gives them a certain advantage for specific tasks such as those that can be performed with IoT devices.
We have integrated an MCP API directly into the node, allowing you to configure a free or proprietary AI model and use it through Neurai's DePIN system, allowing you to connect any device to the AI, regardless of location.
This allows you to take advantage of AI in the following ways:
- Greater efficiency in processing data obtained by the DePIN network.
- Coordination of orders from the client to servers or other devices.
- Creation of files with results from the data received automatically.
- Automated information management systems.
- (For the future): Rental of GPU power through the DePIN network.
- Management of tokenized models under a specific asset.
RWA
Real World Assets (RWA) in the blockchain world refer to the tokenization of physical or tangible assets, allowing them to be represented digitally on the blockchain. This process involves converting real-world assets like real estate, commodities, art, or even revenue streams into digital tokens that can be traded, owned, and managed securely.
Our Assets model allows specific types to be created for asset tokenization with control by the issuer, thus enabling us to cater to different types of customers who want to use our system.
IoT devices and the DePIN network will make it possible to easily establish tokenized real assets and manage them through AI via the creator's private network, but with the possibility of moving these assets through the Neurai network without the need for third-party endorsement.
Added to this tokenization layer is BGrid, a global mapping system using BIP39 words created by our development team, which allows geographical areas to be established for this tokenization when required. With just four words, an area of 27m2 is established, perfect for specifying small areas around the world.
BGrid
BGrid is a hierarchical geographic coordinate system developed by our team that divides Earth's surface into increasingly precise zones using a four-level structure. Unlike traditional latitude/longitude coordinates or other grid systems, BGrid creates 2,048 divisions per level, reaching precision from regional scale (~249,000 km²) down to individual buildings (~29 m²). The system uses alternating division factors—64×32 at odd levels and 32×64 at even levels—to maintain more uniform, square-shaped parcels across different latitudes, addressing the distortion problem that affects many geographic systems.
What makes BGrid particularly powerful for blockchain and IoT applications is its integration with the BIP39 mnemonic word list. Every coordinate can be expressed as memorable words instead of complex numbers—for example, "little airport aunt chief" instead of numerical coordinates. This enables verbal transmission of locations, adjustable privacy (share only the precision you need), and seamless integration with cryptographic standards used in blockchain systems. Whether you're tracking assets, verifying device locations, or building decentralized mapping applications, BGrid provides a human-friendly, privacy-conscious way to reference any place on Earth.
Conclusion
Neurai was born with the idea of achieving secure communication for IoT devices, which is why the DePIN Messaging model was created. With this communication protocol based on Neurai tokens, it is possible to transmit secure and private information between any type of device or person.
Using this communication protocol as a basis, it is possible to build a secure connection model between the real world and the digital world: tokenizing assets of all kinds, transmitting orders to remote devices, AI management of external data, and geolocation with various levels of depth.
But without forgetting that to use the entire Assets system in Neurai, which is the basis of everything, it is necessary to burn coins, and this provides a model that allows balancing the creation of currency via mining and the coins in circulation.